Type of cancer
Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer can be treated with better patient outcomes using NeoTox / Oncemblex technology
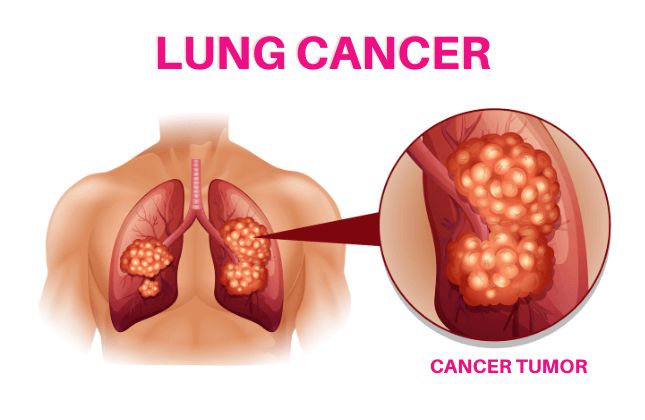
Lung cancer is a leading cause of death and has one of the worst prognoses. Cancer cells that start in the lungs usually grow very quickly to a point where they block airways, or worse yet, spread to other organs and tissues like the brain or liver. The most common symptoms of lung cancer include coughing up blood, chronic fatigue, shortness of breath and chest pain. It is imperative that you see a doctor if you have any one these symptoms on a long-term basis. While there are many treatments available for various types of cancers, this specific post will outline 9 out-of-10 patients who have successfully been treated through surgery followed by chemotherapy.
Your doctor has diagnosed you with lung cancer and now you’re scared that your life will be cut short, but this doesn’t have to be the case! Of all the people diagnosed with lung cancer every year, 90% of them are still alive 10 years after their diagnosis. While there is no way to completely cure lung cancer, it can be treated very successfully in almost all cases, providing treatment options which allow patients to live full, long lives well into old age.
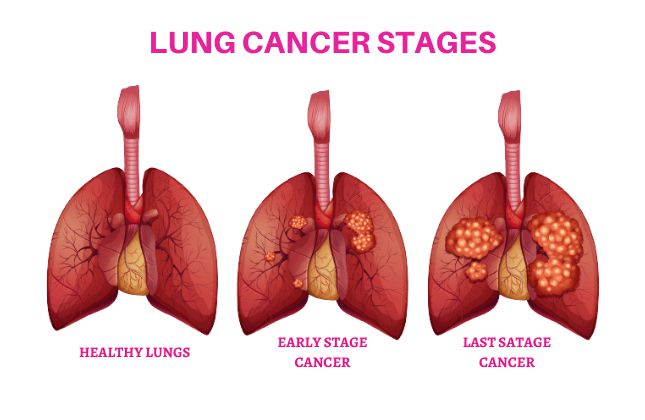

Lung cancer is caused by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lungs. There are different types of lung cancers, classified based on the cells that caused it to start:
- Small cell lung cancer, also called oat cell carcinoma or oat cell tumor, affects less than 5% of people with lung cancer and is more often found in people who smoke a pack a day for more than 20 years. It responds well to chemotherapy.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (small minority) develops into tumors that look like squamous epithelium that line inside the lungs. Tumors may grow into these breathing tubes and interfere with their function. Squamous cells may be found as part of chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Types of cancer
Some top cancers we cure
Breast Cancer
Approximately 85% of breast cancers develop in women with no family history of the disease.

Lung Cancer
Most lung cancer statistics include small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

Prostrate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a disease in which cells in the prostate gland mutate and divide uncontrollably.

Stomach cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as esophageal cancer, It is the eighth most frequent cancer in the world
Skin Cancer
it’s estimated that 90% of all skin cancer can be treated successfully.

Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer most commonly strikes women between the ages of 35 and 44, worldwide,
